Communications
Review Article on the Role of Complex Systems in the Study of Climate Change by CAFE Researchers is Published and Featured
The review article ‘Perspectives on the importance of complex systems in understanding our climate and climate change – The Nobel Prize in Physics 2021’ by CAFE researchers Shraddha Gupta, Nikolaos Mastrantonas, Cristina Masoller and Jürgen Kurths has been published in Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science.
How confident are we in our projections?
We all have experienced (or will experience) the intensity of an extreme meteorological weather event in our lives, for example, persistent high temperatures during a heatwave or intense rainfall due to the development of an extratropical cyclone. Even if these events do not appear very often, they cause severe human and economic losses in the areas they cross.
The CAFE Project Helds its 4th Workshop in Reading (UK)
The 4th CAFE Workshop was held in person at ECMWF, Reading UK, from the 29th to the 31st of March.
ECMWF Director of Forecasts and CAFE Team Member Florian Pappenberger on the Early Warning and EarlyAction Theme
The ECMWF Director of Forecasts Florian Pappenberger considers how ECMWF’s global numerical weather predictions help to provide early warnings and early actions on the occasion of the World Meteorological Day 2022.
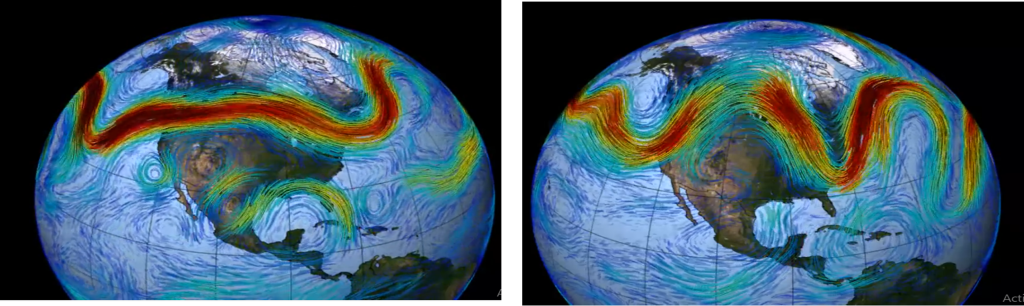
The Rossby Wave Packets
We all have experienced (or will experience) the intensity of an extreme meteorological weather event in our lives, for example, persistent high temperatures during a heatwave or intense rainfall due to the development of an extratropical cyclone. Even if these events do not appear very often, they cause severe human and economic losses in the areas they cross.

Entrevista de Predictia a Riccardo Silini, doctorando de CAFE
Entrevista a Riccardo Silini por parte de predictia, empresa que ofrece soluciones de minería y gestión de datos en el ámbito de la innovación, especialmente en los campos de clima y salud.
